Choice of Programming Languages for Big Data Systems
Ishan Shanware / August 18, 2022
13 min read
Data collection consists of messaging systems which are essential in sending the data from a source to a destination based on the publish/subscribe paradigm.
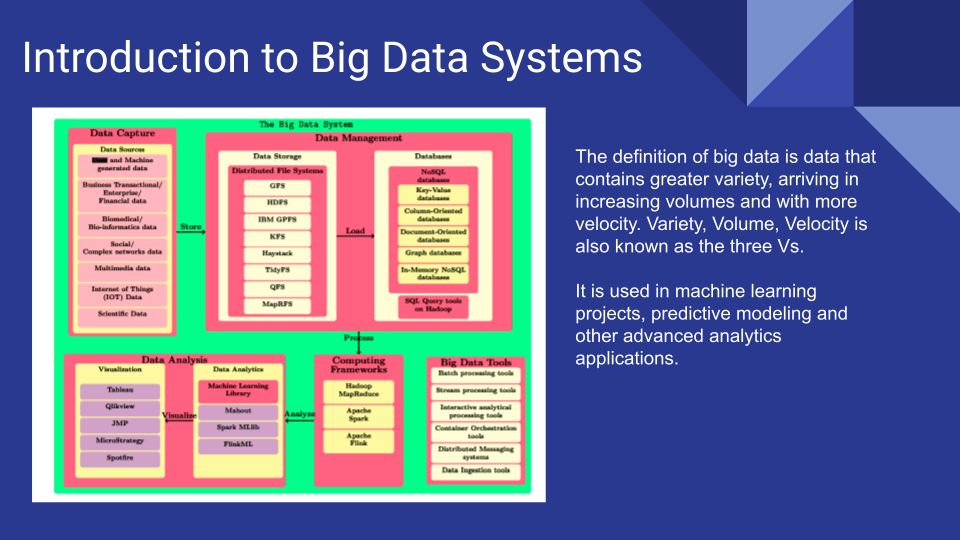
- These message brokerage systems, supply streams of data to stream processing frameworks.
- Stream processing is the practice of taking action on a series of data at the time the data is created.
- Stream processing is closely related to real time analytics, complex event processing, and streaming analytics.
- The data collected has to be managed, which is call Data management.
- It consists of two main parts, data storage and data retrieval. Distributed file systems handles the responsibility of large scale data storage.
- Data retrieval is handled by NoSQL databases.
- The final stage of processing the big data is Data Analysis. Data Analytics and Data Visualization are the two major subtasks of data analysis. In analytics, the data is modeled by using ML algorithms and analyzed using statistical/data mining techniques to obtain hidden patterns from the data.
- Distributed computing is a model in which components of a software system are shared among multiple computers.
- Even though the components are spread out across multiple computers, they are run as one system. They provide improved efficiency and performance.
Key Features for Distributed Systems
- Scalability
- Concurrency
- Transparency
- Fault tolerance
Distributed Storage and Distributed Processing help address the 4 Vs.
- Ideas of distributed computing solve latency issues with management of large quantities of data.
- Also helps to store, retrieve, and update data in well coordinated manner.
- Distributed technologies help manage and process higher variety of data streams.
- When dataset is more than few terabytes, it is necessary to use a distributed system so that can be partitioned across machines.
Programming Languages for Distributed Systems
- Communication and Synchronization between parallel parts of the program
- Exception Handling mechanism brought about by partial failure Scale, does the language maintain and support the large scale programs development?
- Modularity, does language supports programs decomposition into suitable units? Reusability, does the language supports effective program units' reuse?
- Portability, does the language support portable code writing? Or does the code port from one platform to a dissimilar platform without majorchange?
- Extendibility relates to the possibility of developing the language and its implementation, existence of function libraries, class libraries,... etc There are many other important features as well…..
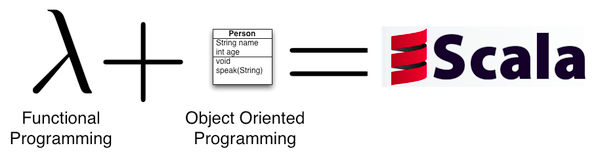
Functional programming in Distributed Systems
Concurrency in Distributed Systems
- Applications and Services can offer resources that can be shared by clients. Many clients will access shared resource at the same time concurrency is a pretty complex subject.
- Threads and locks, avoiding issues like race conditions and deadlocks make concurrent programs difficult to right.
Problem with OOPs approach
- Mutable State
- Object’s method is supposed to mutate it’s internal state Mutex lock introduces the problem deadlocks To solve the problem, Object oriented code become extremely lengthy
- Functional Programming Approach
- Purity
- Avoids side-effects
- Immutability Functional languages have data types that don’t mutate.
- Erlang and Clojure are 2 functional programming languages used heavily to build distributed systems.
- Erlang is a dynamically typed and often known as a concurrent programming language, and fault tolerance.
- Clojure is also a dynamically typed language, which is known for it’s immutable data structures.
- Purity
Java Code
public void greetingsFromSanta(int n) {
int i = 0;
while (i < n) {
System.out.print("Ho! ");
i = i + 1;
}
}
###Clojure Code
(defn greetings-from-santa [n]
(if (> n 0)
(do
(print "Ho! ")
(greetings-from-santa (dec n)))))
Data Stream Processing Frameworks and Message Brokerage Systems
Apache Storm
- Released by Twitter, Apache Storm is a distributed, open-source network that processes big chunks of data from various sources. The tool analyzes it and updates the results to a UI or any other designated destination, without storing any data.
- Written in Clojure
- generic, immutable data structures and pure functions.
- by Clojure's generic data structures, it is easy to distribute work or data across multiple machines
- When functions (or declarative expressions, e.g. database queries) can be expressed as data structures, they are easier to compose and distribute
RabbitMQ
- RabbitMQ is one part of Message Broker that implemented Advance Message Queue Protocol (AMQP), that help your application to communicate each other, when you extends your application scale.
- Used for data collection from application and connected with apache storm for data processing.
- Written in Erlang
- Based on actor model of concurrency
- Let it crash! philosophy
Data Storage and Management
- Apache Hadoop is a collection of open-source software utilities that facilitates using a network of many computers to solve problems involving massive amounts of data and computation.
- It is designed to scale up from single servers to thousands of machines, each offering local computation and storage.
- It provides a software framework for distributed storage and processing of big data.
- The core of Apache Hadoop consists of a storage part, known as Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), and a processing part which is a MapReduce programming model.
- Apache Hadoop is written in Java programming language.
Data Management Frameworks
MapReduce
- It is a programming model and an associated implementation for processing and generating big data sets.
- MapReduce libraries have been written in many programming languages, with different levels of optimization.
- It has its roots in functional programming.
- Mapreduce uses two main functions Map and Reduce.
- Both are higher order functions, on which functional programming is based.
- Both functions also have no side effects, which enables concurrency. This is also a major feature of functional programming
- Hadoop uses MapReduce framework for data management. An example of how the mapreduce functions work.
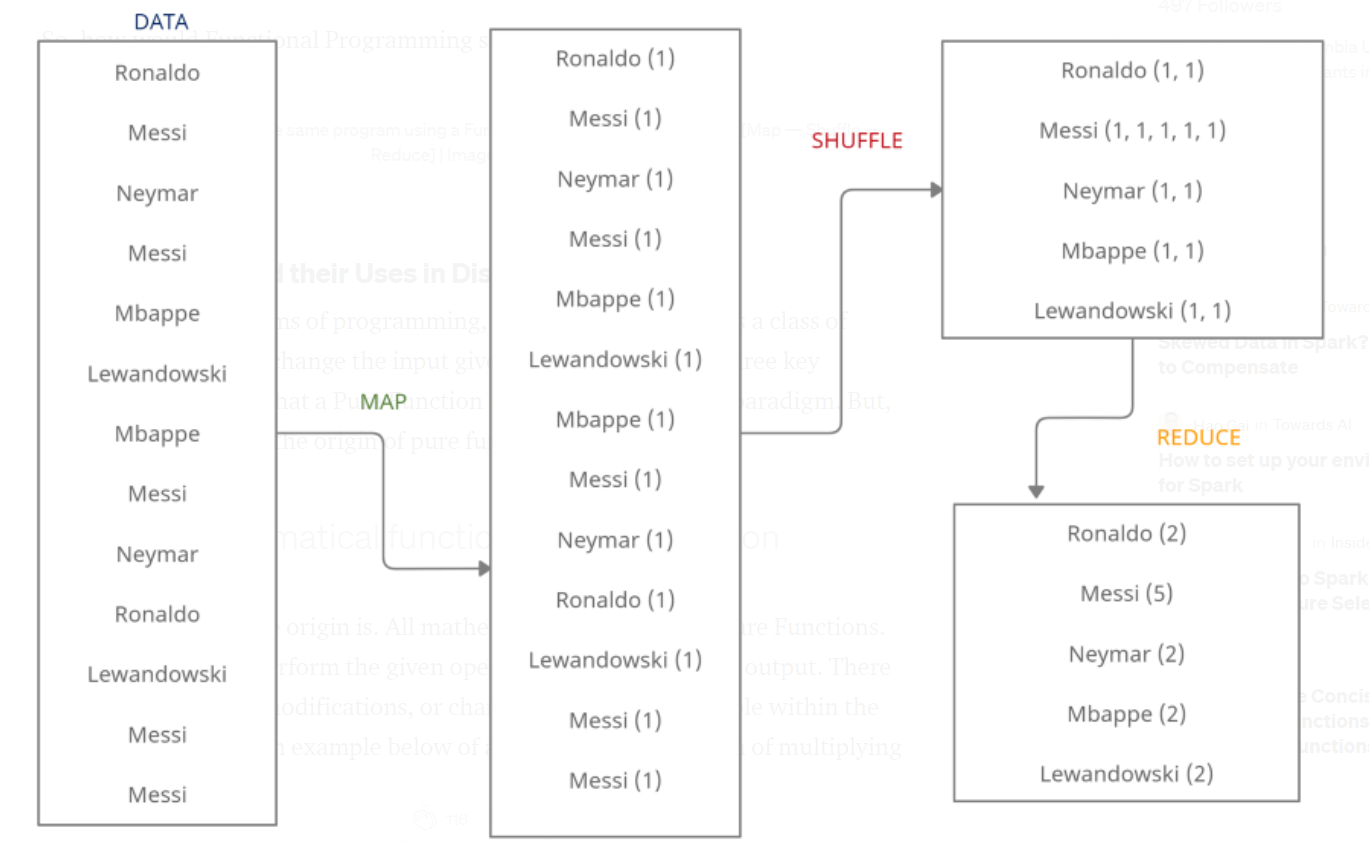
Compute Frameworks
ROOT
- Object Oriented Framework built on top of C++
- Used for storing and processing large amounts of data produced in high energy physics.
- The TFile class in ROOT is used to store files.
- Special class - TTrees for storing objects of same class objects.
- TTree class is optimised to reduce disk space and enhance access speed.
Apache Spark
High performance, general purpose distributed computing framework written in scala which is a statically typed functional programming language.
RDD (Resilient Distributed Datasets) are the fundamental data structure of Spark.
RDDs are distributed collections that are statically typed and lazily evaluated.
RDDs come with higher order functions like map, reduce, join and filter to manipulate the distributed datasets.
Higher order functions applied on RDDs are lazily evaluated.
Garbage Collection
- Many popular systems for processing “big data” are implemented in high-level programming languages (Java and Scala) and run atop JVM with automatic memory management via garbage collection (GC).
- However, high object churn and large heap sizes put severe strain on the garbage collector.
- As a result, applications underperform significantly GC increases the runtime of typical data processing tasks by up to 40%.
- Native languages like C/C++ provide a tighter control on memory and performance characteristics of the application than languages with automatic memory management.
- A well written C++ program that has intimate knowledge of the memory access patterns and the architecture of the machine can run several times faster than a Java program that depends on garbage collection.
- For these reasons, many enterprise developers with massive scalability and performance requirements tend to use C/C++ in their server applications in comparison to Java.
For example, Bloomberg uses Python for much of its data science exploratory work that goes into services delivered in the Bloomberg Terminal. But when it comes to writing the actual programs that feed data to customers in real time, it turned to C++.
Data Analysis Data Analysis is the final stage of the processing of the big data.
There are two subtasks in the task of Data Analysis
- Data Analytics
- Data Visualization.
In analytics, the goal is to find/predict patterns by modeling the data using ML algorithms and analyzed using statistical/data mining techniques.
- The platforms and paradigms used to process ML-related data have changed tremendously over the past decade, due to a range of performance and programmability issues with MapReduce-based systems and the need to execute ML workloads on modern hardware like GPUs.
- Mahout and MLlib are the two most popular distributed libraries. Mahout -> Apache Hadoop MLlib -> Apache Spark
Mahout
- Mahout is one of the more well-known tools for ML. It is written in Java and Scala and used for creating scalable machine learning algorithms.
- The algorithms of Mahout are written on top of Hadoop, so it works well in distributed environment. Mahout uses the Apache Hadoop library to scale effectively in the cloud.
- Classification algorithms currently offered in Mahout are Logistic Regression, Naïve Bayes, Random Forest, Hidden Markov Models, and Multilayer Perceptron.
- It also includes several MapReduce enabled clustering implementations such as k-means, fuzzy k-means, Canopy, Dirichlet, and Mean-Shift.
- Mahout is probably the best-known framework for collaborative filtering tools, also known as recommendation engines.
MLlib
- Apache Spark consists of a distributed machine learning library of algorithms known as MLlib. It is written in Scala and use native (C++ based) linear algebra libraries on each node, MLlib includes Java, Scala, and Python APIs.
- MLlib covers the same range of learning categories as Mahout, and also adds regression models, which Mahout lacks.
- The library targets large-scale learning settings that benefit from data-parallelism or model-parallelism to store and operate on data or models.
- MLlib consists of fast and scalable implementations of standard learning algorithms for common learning settings including classification, regression, collaborative filtering, clustering, and dimensionality reduction.
- It also provides a variety of underlying statistics, linear algebra, and optimization primitives
Julia for ML and Data Analysis
- Python’s methods require serialization and deserialization of data for parallelizing between threads whereas Julia’s parallelization is much more refined.
- Julia uses multiple dispatches as its central programming paradigm.
It supports parallelism in three primary levels, namely
- Julia coroutines (green threading), - Multi-threading, - multi-core or distributed processing.
- Julia is not interpreted and uses just-in-time (JIT) compilation and type declaration.
- It’s speed is almost as same as native languages like C/C++.
Twitter and Scala
- Twitter’s Big Data Ecosystem (Understanding Current Choice of Languages)
- Process approximately 400 billion events in real time and generate petabyte (PB) scale data every day.
- They organize the infrastructure and tools of a comprehensive and robust big data platform into three categories - data processing, data storage, and data consumption.
- Twitter was once the largest Ruby user in the world, however in recent years it has moved a lot of code to the JVM.
- Both languages are readable and concise, Object Oriented, decomposable.
- Concurrency
- Ruby does not have inbuilt support for concurrency, comes from external libraries. Event Machine library, for concurrency.
- Causes long chain of callbacks.
- Scala has built in concurrency models like the actor model and futures.
- Ruby does not have inbuilt support for concurrency, comes from external libraries. Event Machine library, for concurrency.
- Type Systems
- Ruby’s dynamic typing allows for rapid prototyping.
- Scala’s Static typing makes the code clearer, and catches error for production level.
- Performance
- Expectations
- Higher Throughput and Better CPU Usage
- Scala performs better than ruby in throughput and hardware utilization.
- Expectations
Functional Programming at Twitter with Scala
- Twitter structures concurrent programs around futures
- To handle events on large chunks of streaming data, futures are used
- Together with HOFs, Futures can be used to create more complex operations
- permits defining a future as a function of another, such that the two are executed sequentially.
- For example, when a user sends a Tweet, we first need to see if that user is within the hourly rate limits before writing the Tweet to a database.
Functional Programming using Futures in Scala
val count:Future[Int] = getCount()
count.respond {
case Return(value) =>
println(s"The count was $value")
case Throw(exc) =>
println(s"getCount failed with $exc")
}
def isRateLimited(user:Long):Future[Boolean] = ...
def writeTweet(user:Long, tweet:String):Future[Unit] = ...
val user = 12L
val tweet:String = "just setting up my twitter"
val done:Future[Unit] =
isRateLimited(user).flatMap {
case true => Future.exception(new RateLimitingError)
case false => writeTweet(user, tweet)
}
Scala For Big Data
- Scala is all about scalability and fault tolerance, and that means it works well with huge amounts of data.
- A lot of data analytics software offers support for Scala, making it easy to integrate the software into your system.
- It’s one of the standout features of Scala because something like Ruby, which Twitter used before transition to Scala, doesn’t have the ability to support big data effectively.
- Apache Spark is implemented in Scala.
- Make use of HOFs
- Apache Kafka another message brokerage system is also written in Scala.
- Apache Kafka is a distributed data store optimized for ingesting and processing streaming data in real-time.
- A Kafka topic is an immutable log of events (sequences).
- Immutable Classes of Scala help make streaming data
Alternate and Rising Languages
Golang for developing Big Data Frameworks
- GO has been developed for the modern times.
- GO is built for multi core machines to maximise parallelism for the concurrent programs.
- GO has C like syntax, is statically typed and has a super fast compiler.
- GO overcomes the shortcomings of C++ and includes features like garbage collector, memory safety and structural typing.
- Difficult to maintain code consistency in Scala, easier in GO.
Julia for Data Analysis
- As compared to Python and R, Julia is a relatively new language. Python was not necessarily designed with parallel computing in mind.
- Parallel computing is becoming more and more important and more and more widely-used every single day especially for big data systems.
- Julia is built for scalability and speed of operations when handling large data sets.
- Julia is an excellent choice for numerical computing and it takes lesser time for big and complex codes. Julia undoubtedly beats Python in the performance and speed category.
- But there are certain drawbacks of Julia as well
- Smaller community
- Less ML libraries
References
Holden Karau, Rachel Warren, High Performance SparkOreilly. René Brun, Fons Rademakers, Suzanne Panacek, Root an object oriented data analysis framework. CERN. Marius Eriksen, Functional at Scale Rao et al, The big data system, components, tools and technologies a survey Debasish Ghosh, Programming languages impact on development of distributed systems